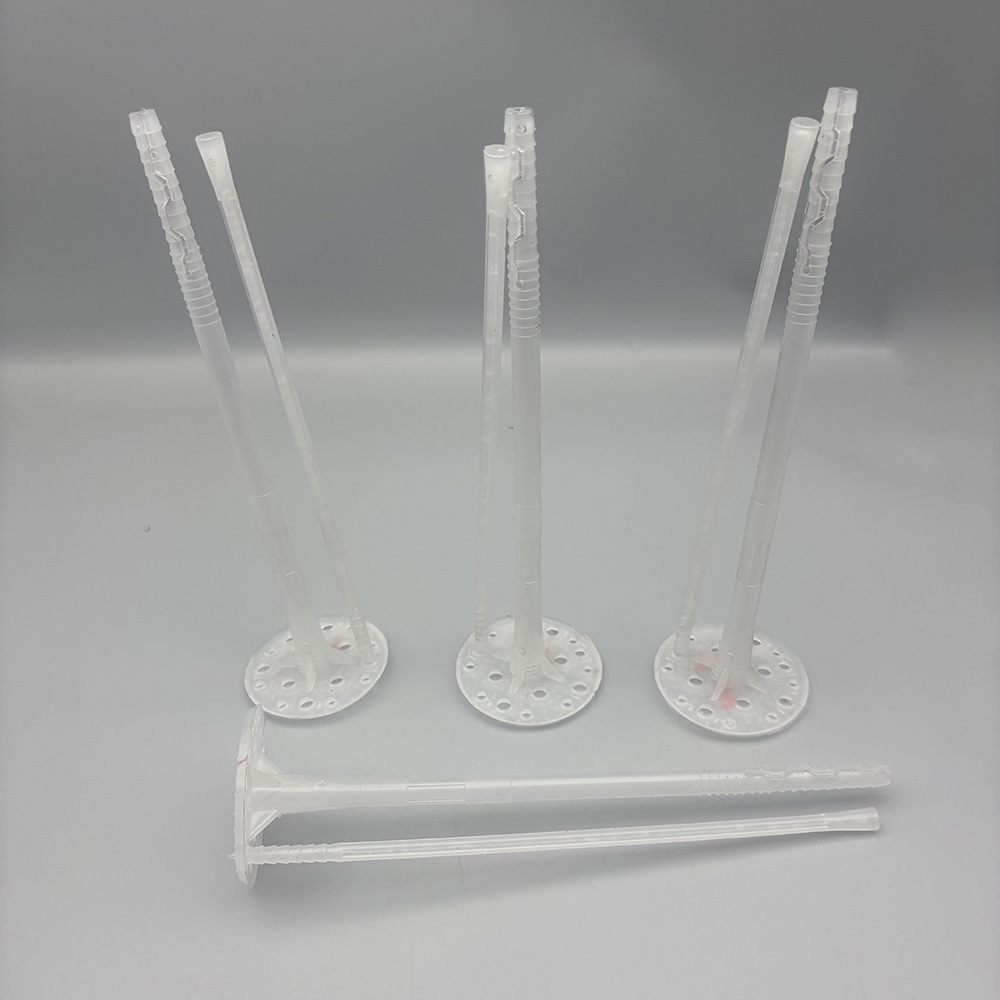
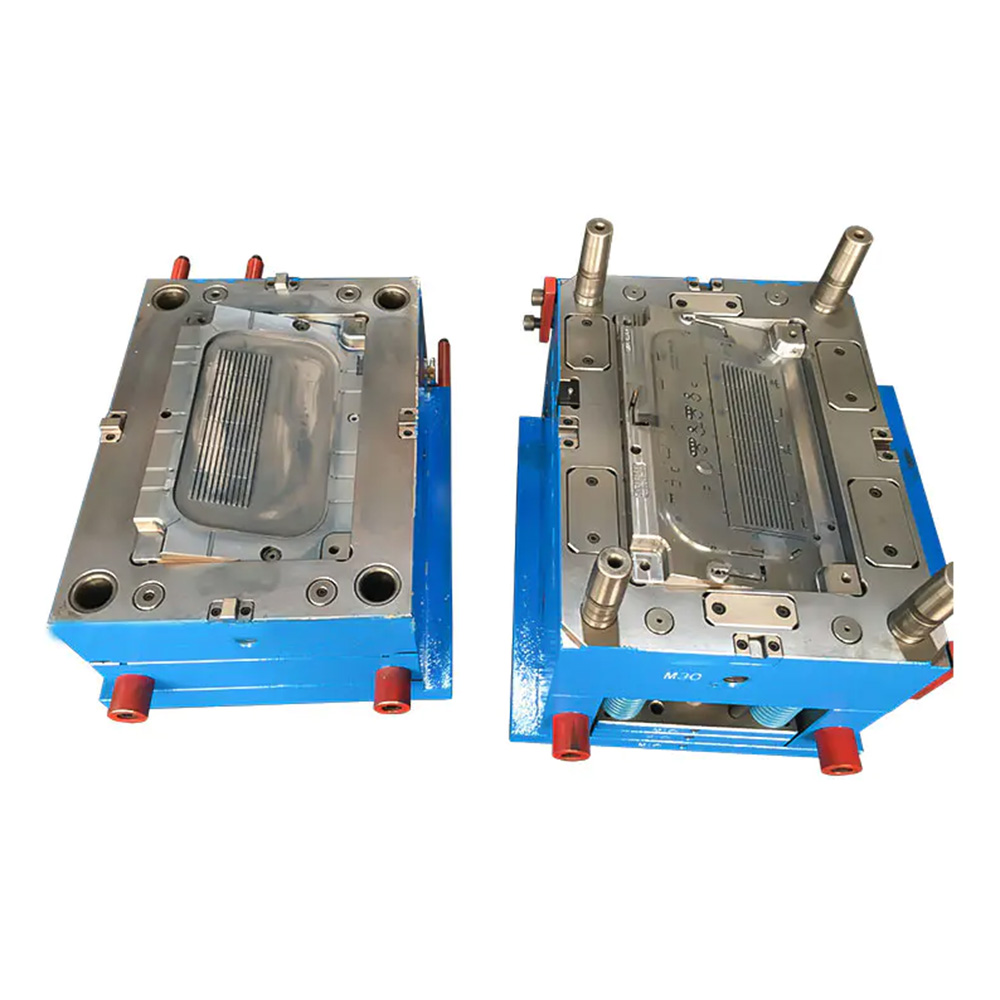
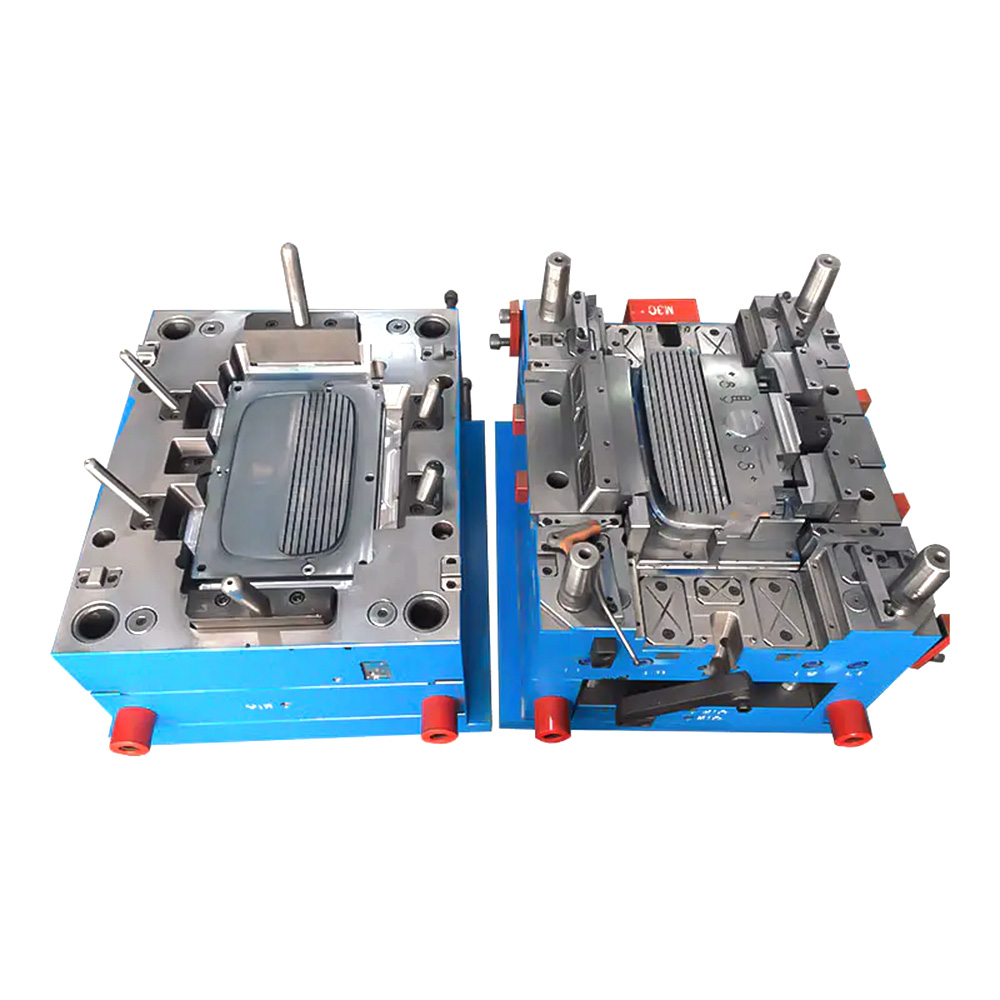
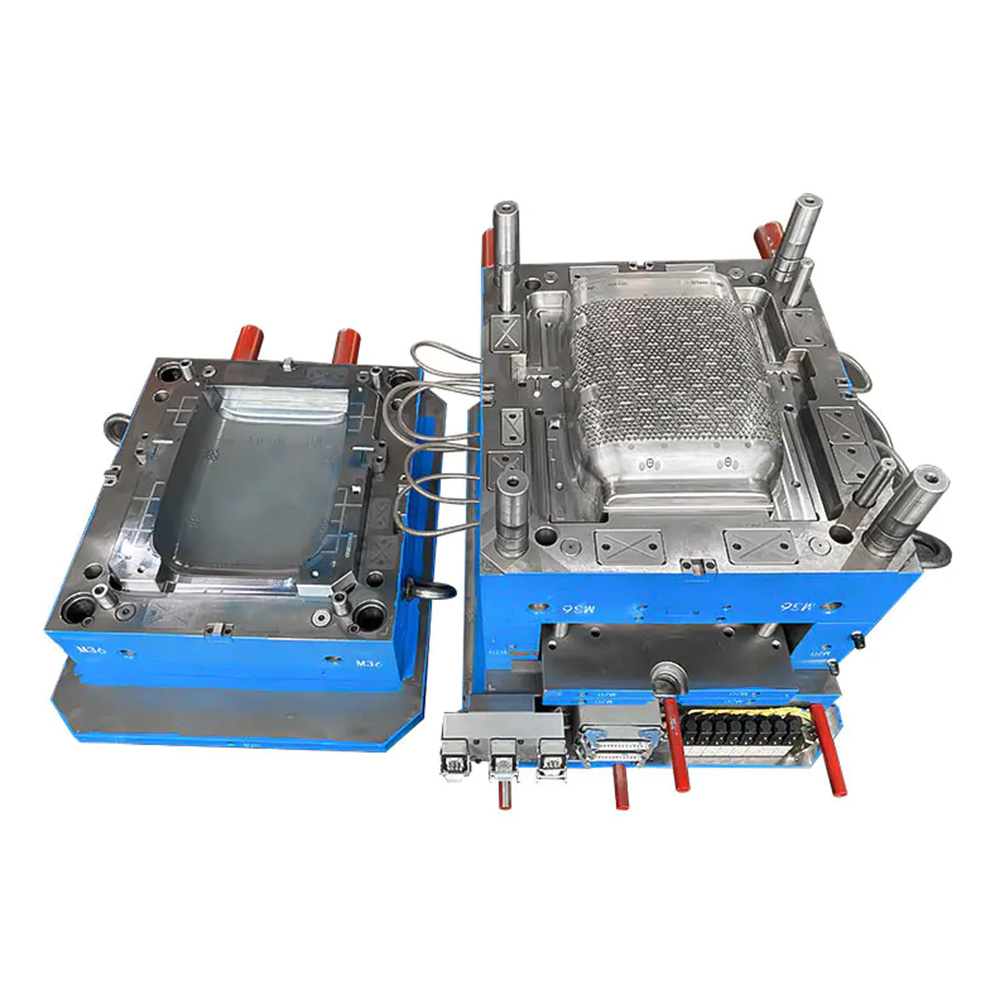
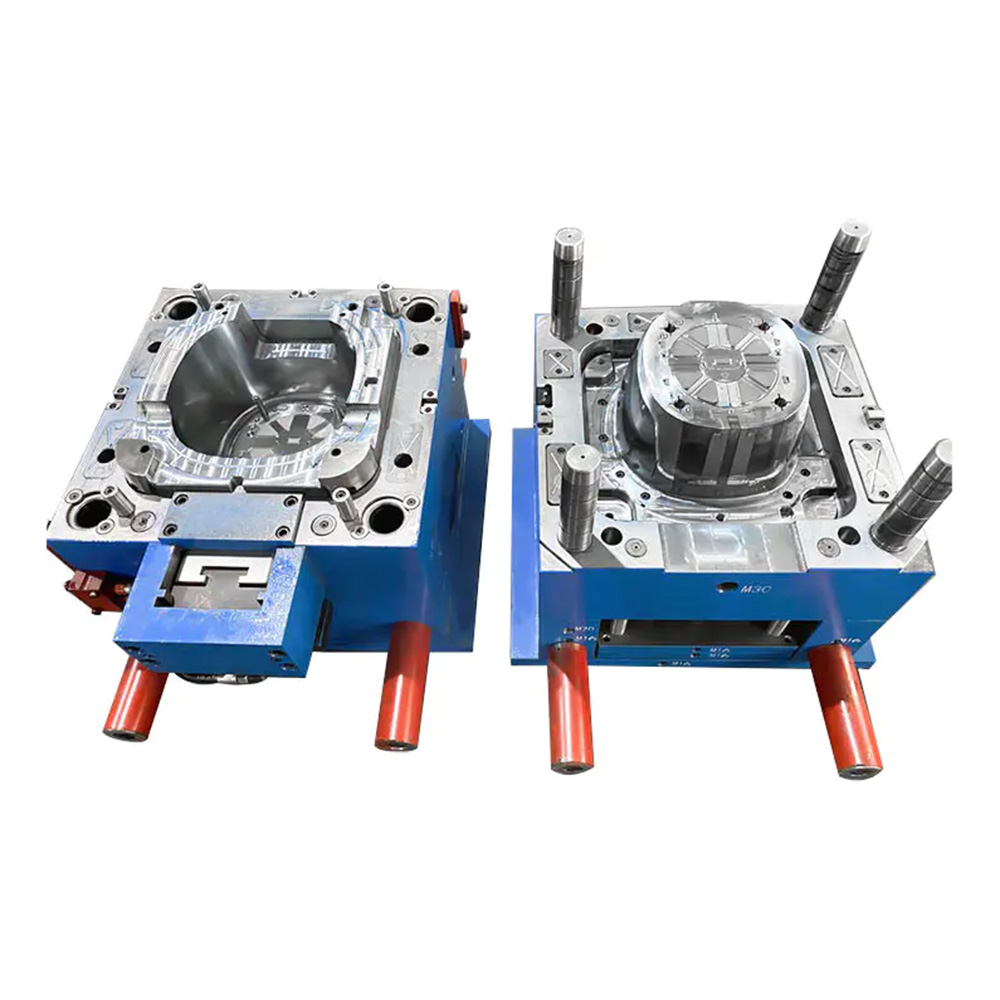
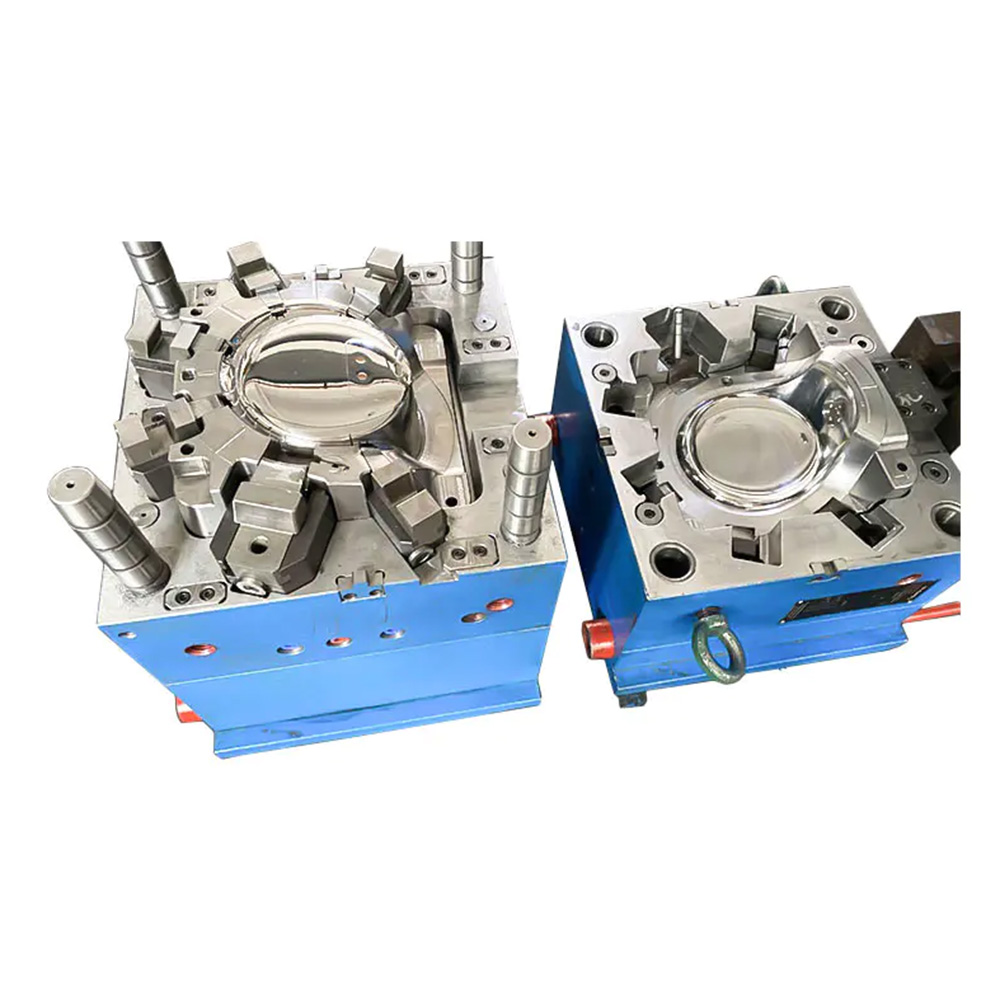
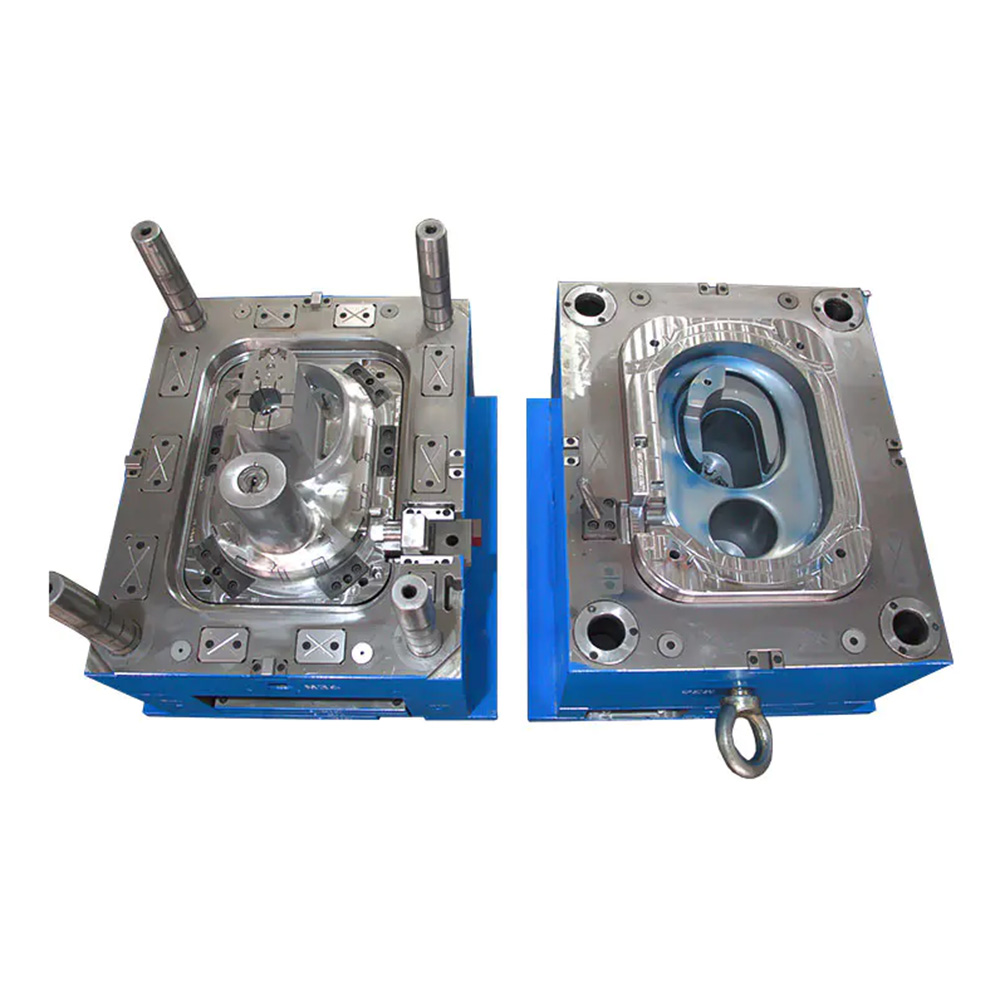
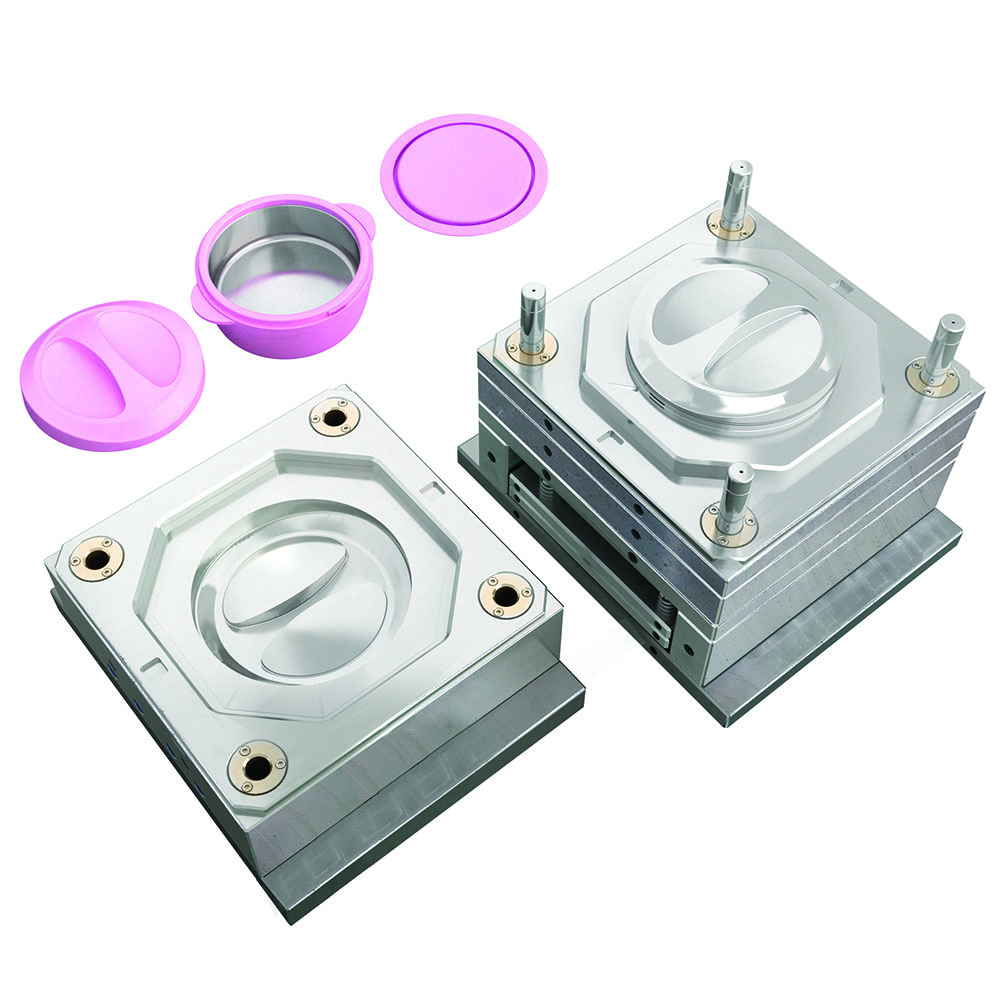
Expansion screw wall plug mold
An Expansion Plug Mold (also commonly known as a Wall Plug Mold, Anchor Mold, or Fischer Plug Mold) is a highly specialized type of injection mold designed for the high-volume, precision manufacturing of the plastic component of an expansion anchor system. This component, the expansion plug, is the core element that, when paired with a screw, provides a secure fastening in base materials like masonry, concrete, and drywall.
This type of mold falls under the category of high-cavitation, high-speed production molds, where precision, durability, and efficiency are paramount.
High Cavitation: These molds are almost always multi-cavity molds (e.g., 16, 32, 64, or more cavities) to maximize output and minimize per-part cost.
Wear-Resistant Materials: Core and cavity inserts are made from high-grade, pre-hardened or through-hardened tool steels (such as P20, H13, or Stainless Steel grades) to withstand the abrasive nature of certain plastics and the high production volumes.
High-Precision Machining: The internal undercuts and delicate segments of the plug require ultra-precise machining using CNC, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), and Wire-Cutting technologies.
Automation-Optimized: The mold is designed for fully automated production cycles, including robotic part extraction and conveying systems.
1. Core Functions and Target Products
Functions: Molten plastic (such as nylon PA6, polypropylene PP, etc.) is injected into a mold cavity under high pressure. After cooling and solidification, it forms a plastic expansion tube (wall plug) of a specific shape and size.
Target Products: The plastic tube we insert into holes drilled in walls in our daily lives is produced by this type of mold. It is an indispensable part of an expansion screw set.
Target Products: The plastic tube we insert into holes drilled in walls in our daily lives is produced by this type of mold. It is an indispensable part of an expansion screw set.
2. Mold Structure and Components A typical expansion screw wall plug mold consists of the following major systems: a. Molding System This is the core of the mold, directly determining the shape of the wall plug. Cavity: Usually located on the fixed mold side of the mold, forming the outer surface of the wall plug, the head flange, and the threads. Core: Located on the moving mold side of the mold, forming the inner hole and internal structure of the wall plug. Because wall plugs typically have internal undercuts to enhance expansion, the core structure is often complex and may require a slider or angled ejector mechanism for demolding. b. Gating System: The channel through which plastic enters the mold cavity. Main Runner: The section connecting the injection molding machine nozzle to the runners. Runners: Guide the plastic from the main runner to the individual cavities. Gate: A small channel connecting the runner and the cavity. For slender products like wall plugs, point gates or submarine gates are often used for automatic removal, reducing manual labor and post-processing.
c. Ejection System
After the product cools, it is removed from the core.
c. Ejection System
This system removes the product from the core after it has cooled.
Ejector pin、Ejector tubeorPush plate: Because the wall plug is tubular and has a complex internal structure, the design of the ejection system is crucial. It needs to eject the product smoothly and evenly, avoiding whitening or deformation.
d. Cooling system
To shorten the production cycle, the mold has complex cooling water channels. Through circulating cooling water, the molten plastic is cooled and solidified quickly and evenly, ensuring stable product quality and production efficiency.
e. Guiding and Positioning System Guide Posts and Guide Sleeves: Ensure precise alignment of the moving and fixed molds during mold closing, preventing misalignment of the cavity and core, and ensuring uniform product wall thickness. Positioning Blocks: Provide additional precise positioning. f. Venting System During plastic filling, air inside the cavity needs to be vented. Tiny venting grooves are typically created at the parting line or inserts to prevent defects such as scorching or incomplete filling caused by trapped air.
FAQS
A: We are a specialized manufacturer of precision molds, with a primary focus on Cold Fan (Air Cooler) Molds and a comprehensive range of Home Appliance Molds. This includes molds for components in refrigerators, air conditioners, washing machines, and small kitchen appliances.
A: Absolutely. We provide an end-to-end solution, from initial design and engineering (DFM), 3D modeling, and precision machining to mold trials, sampling, and final production support. We are your one-stop shop for a complete mold project.
A: We ensure quality through a multi-step process: using high-grade mold steels, operating state-of-the-art CNC machining centers, and implementing a rigorous Quality Control (QC) system. Every mold undergoes precise measurement and a thorough trial process to verify its performance and the quality of the parts it produces.
A: Yes, we highly recommend and provide DFM analysis at the beginning of every project. Our engineering team will review your part design to optimize it for manufacturability, suggesting improvements for moldability, cost-efficiency, and part performance.
A: Lead times vary depending on the mold's complexity and size. For a standard cold fan or home appliance mold, the typical lead time ranges from 4 to 8 weeks. We will provide a detailed project timeline with a specific completion date after reviewing your technical requirements.
A: Of course. We always produce and provide initial sample parts (T1) from the new mold for your approval. This allows you to verify dimensions, appearance, and function before we proceed to mass production.
A: Our molds are designed to process various common plastics used in appliances, including ABS, PP, PS, PC, and PA (Nylon). We select the appropriate mold steel and design the mold structure based on your specific material choice.
A: We offer comprehensive after-sales support. This includes providing detailed mold maintenance guidelines and offering repair and modification services to ensure your mold maintains peak performance and a long service life, maximizing your return on investment.
A: Our key differentiator is our dual specialization. We are not just general mold makers; we have deep, specific expertise in both the highly technical Cold Fan category and the broad Home Appliance market. This focus allows us to provide superior engineering solutions and value for our clients in these sectors.
A: We take IP protection extremely seriously. We are willing to sign a strict Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) before any project discussion. All your designs, drawings, and data are treated with the utmost confidentiality and are never shared with any third party.
Standard Process for Ordering Injection Molds:
| Phase | Stage | Key Activities / Deliverables | Responsible Party | Purpose & Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Project Initiation & Feasibility | 1. RFQ (Request for Quotation) | • Provide detailed product design (3D CAD, 2D drawings). • Specify requirements: material, annual volume, target part cost, lead time. | Customer | Establishes the project baseline and allows the mold supplier to provide an accurate quotation. |
| 2. Design for Manufacturability (DFM) Review | • Mold supplier analyzes the product design for moldability. • Provides DFM report with suggestions on draft angles, wall thickness, gate locations, shrinkage, etc. | Mold Supplier (with Customer approval) | Critical for avoiding costly mold modifications later. Ensures the part is optimized for injection molding. | |
| 3. Quotation & Commercial Agreement | • Submit a detailed quotation covering mold cost, payment terms, and project timeline. • Negotiate and sign a purchase order (PO) and/or contract. | Mold Supplier & Customer | Formalizes the commercial agreement and project scope. | |
| Phase 2: Engineering & Design | 4. Mold Design Finalization | • Create detailed mold flow analysis. • Finalize mold design (2D layout, 3D model) including: cavity/core, slider/lifter mechanisms, cooling system, ejection system. • Customer approves final mold design. | Mold Supplier (with Customer approval) | The mold design is the blueprint for manufacturing. Approval at this stage is crucial. |
| 5. Material & Component Sourcing | • Procure approved mold base, steel (e.g., P20, H13, Stainless for corrosive materials), and standard components (hot runners, ejector pins, etc.). | Mold Supplier | Using quality materials is essential for mold life and performance, especially for high-volume家电 (home appliances). | |
| Phase 3: Mold Manufacturing | 6. Machining & Fabrication | • CNC machining of cavity and core. • EDM, wire cutting, grinding, and polishing. • Fabrication of all mold components. | Mold Supplier | The physical creation of the mold. Regular progress updates (e.g., photos) are often provided. |
| 7. Fitting & Assembly | • Assemble all machined components into the mold base. • Check for proper fit and function of all moving parts (sliders, lifters, ejection). | Mold Supplier | Ensures the mechanical integrity of the mold before the first trial. | |
| Phase 4: Sampling & Validation | 8. T1 (First Trial) & Initial Sample Report (ISIR) | • Conduct the first mold trial on an injection molding machine. • Measure and inspect T1 samples. • Provide a detailed T1 trial report with samples, pictures, and data (dimensions, short shots, etc.). | Mold Supplier | The first physical verification of the mold's performance. Identifies initial issues. |
| 9. Sample Evaluation & Engineering Changes | • Customer evaluates T1 samples for dimensions, appearance, and function. • Provide formal feedback for any required mold modifications (ECN - Engineering Change Notice). | Customer | Customer's turn to validate the part against their design and quality standards. | |
| 10. Mold Modification & Further Trials (T2, T3...) | • Implement approved ECNs. • Conduct subsequent trials (T2, T3) until samples meet all approval criteria. • Submit PPAP (Production Part Approval Process) samples if required. | Mold Supplier (with Customer feedback) | Iterative process to refine the mold until it produces acceptable parts. | |
| Phase 5: Final Approval & Delivery | 11. Final Sample Approval | • Customer issues a formal Sample Approval Sheet or sign-off. | Customer | Official confirmation that the mold produces parts to specification. |
| 12. Mold Finish & Documentation | • Apply final surface finishes (e.g., texture, polish). • Prepare and deliver final documentation: mold design drawings, maintenance manual, mold certificate. | Mold Supplier | Prepares the mold for production and provides necessary documentation for its future maintenance. | |
| 13. Shipment & Delivery | • Arrange secure packaging and shipment of the approved mold to the production facility. • Settle final payment as per the agreement. | Mold Supplier & Customer | Transfer of ownership and physical asset. | |
| Phase 6: Post-Delivery Support | 14. Production Support & Warranty | • Provide technical support during production ramp-up. • Honor the agreed warranty period for workmanship and materials. | Mold Supplier | Ensures a smooth transition to mass production and protects the customer's investment. |